The Successful Venture Life Cycle Entrepreneurial Financial Management
Created By : Helen Priscilla – 2201775575 / LB-02
Venture life cycle begins in the development stage, has various growth stages, and “ends” in a maturity stage.
The 5 life cycle stages are :
- Development Stage à a phase that a company goes through during the preliminary or early stage of its corporate life.
- Startup Stage à the stage where you start selling products or services.
- Survival Stage à the state where we must maintain our products and services to consumers so that the business situation remains stable.
- Rapid-growth Stage à the stage at which product or service sales increase rapidly, but still experiencing the stage of survival.
Early-maturity Stage à this phase marked by consolidation, where the entrepreneur is faced by a dilemma of having to choose between whether to keep expanding or make an exit.
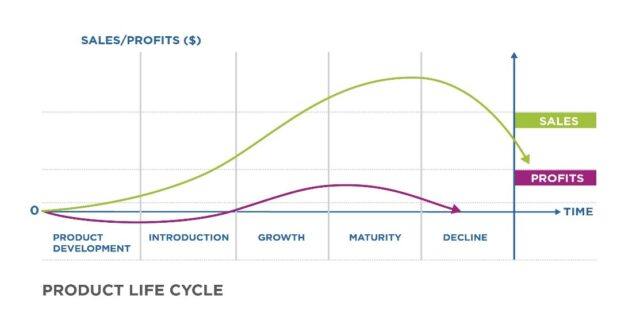
Market Size is the number of individuals in a certain market who are potential buyers and/or sellers of a product or service.
Business ideas can be protected with :· Patents ( protect copyrighted works )· Trade secrets ( protect recipes ) · Trademarks ( protect the logo ) · Copyright ( protect written works, for example : books and songs ) S W O T is a strategic planning technique used to help a person or organization identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to business competition or project planning.
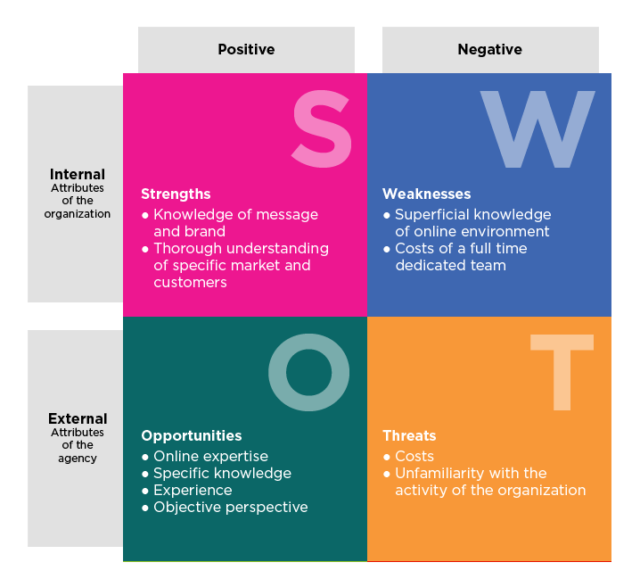
Strenghts : characteristics of the business or project that give it an advantage over others.Weaknesses : characteristics of the business that place the business or project at a disadvantage relative to others.Opportunities : elements in the environment that the business or project could exploit to its advantage.Threats : elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the business or project.
Baca Juga: Komoditas Ekspor Pertanian Porang di Era Digital
Strengths and weaknesses (internal factors within an organization) :
-
Human resources — staff, volunteers, board members, target population
-
Physical resources — your location, building, equipment
-
Financial — grants, funding agencies, other sources of income
-
Activities and processes — programs you run, systems you employ
-
Past experiences — building blocks for learning and success, your reputation in the community
Opportunities and threats (external factors stemming from community or societal forces) :
-
Future trends in your field or the culture
-
The economy — local, national, or international
-
Funding sources — foundations, donors, legislatures
-
Demographics — changes in the age, race, gender, culture of those you serve or in your area
-
The physical environment —is your building in a growing part of town? Is the bus company cutting routes?
-
Legislation — do new federal requirements make your job harder…or easier?
-
Local, national, or international events
A SWOT analysis can be used to:
-
Explore new solutions to problems.
-
Identify barriers that will limit goals/objectives.
-
Decide on direction that will be most effective.
-
Reveal possibilities and limitations for change.
-
To revise plans to best navigate systems, communities, and organizations.
-
As a brainstorming and recording device as a means of communication.
To enhance “credibility of interpretation” to be used in presentation to leaders or key supporters.


Comments :