Unsupervised Learning for Newbie
In the era of technology and big data, artificial intelligence has become a pilar in processing information to generate useful ideas. One of the key example of machine learning is unsupervised learning. Unlike supervised learning, which requires labeled data, unsupervised learning deals with raw, unlabelled data to discover hidden patterns or structures.
Unsupervised learning is a machine learning method where algorithms are trained using unlabelled data. These algorithms aim to identify patterns, relationships, or specific structures within the data. The main techniques in unsupervised learning include clustering and dimensionality reduction.
K-Means Clustering is one of the most popular clustering algorithms, dividing data into K predefined clusters. The algorithm works iteratively by assigning data points to the nearest centroid and recalculating centroids until they stabilize. K-Means++ is an improved version that strategically initializes centroids to speed up convergence. Another approach, the Mean Shift algorithm, does not require specifying the number of clusters in advance. It treats data points as a distribution and iteratively shifts centroids towards regions of higher density until convergence. Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) assume data is generated from multiple Gaussian distributions and models this as a weighted sum of these distributions. It uses algorithms like Expectation-Maximization (EM) to estimate parameters, making it flexible for modelling complex data. Dimensionality reduction techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding (t-SNE) help reduce the number of features in a dataset while retaining important information. PCA identifies the most influential variables, while t-SNE visualizes high-dimensional data in two or three dimensions.
Unsupervised learning finds numerous applications across industries. In business, companies use clustering algorithms to group customers based on shopping behaviour, preferences, and demographics, helping design more targeted marketing strategies. In cybersecurity, algorithms like Isolation Forest and DBSCAN identify outliers or suspicious activities, aiding in the detection of potential cyber-attacks. Platforms like Netflix and Spotify rely on unsupervised learning to analyse user behaviour and suggest personalized content. Data compression techniques such as PCA help reduce the dimensionality of large datasets, improving data processing efficiency. In the stock market, algorithms like GMM model stock price fluctuations by identifying patterns in historical data, assisting investors in making data-driven decisions. Furthermore, unsupervised learning is crucial for image processing, where it is used in object detection and image segmentation, key for computer vision applications.
Unsupervised learning offers incredible flexibility in discovering hidden patterns and structures in unlabelled data. With its diverse applications — from marketing and cybersecurity to stock analysis and computer vision — it plays a vital role in advancing artificial intelligence. As technology evolves, mastering unsupervised learning concepts becomes essential for those pursuing careers in data science and AI.
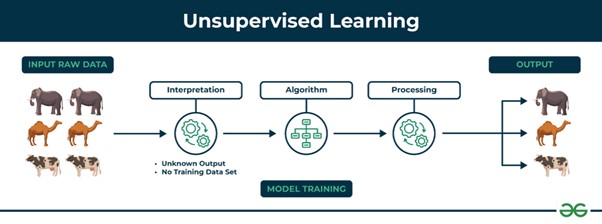 Picture From: https://sis.binus.ac.id/2024/10/24/supervised-vs-unsupervised-learning/
Picture From: https://sis.binus.ac.id/2024/10/24/supervised-vs-unsupervised-learning/



Comments :