Importing SQL Libraries Into JavaFX with Maven: A Step-by-Step Guide
Preliminary of Java:
Java is a powerful and versatile programming language that is widely used. Java is designed around the concept of “objects”, which are bundles of data and behavior, a concept that promotes modularity and code reusability. Java is also used in a wide range of applications, including web applications, mobile applications (especially Android), enterprise software, big data processing, embedded systems, and game development. Java code also can run on various operating systems.
Preliminary of Java with Maven:
Java with Maven or another word can be said that Apache Maven is a powerful build automation tool, which is mainly used for Java projects.
Maven has the objective to simplify the build process by providing a standardized way to manage dependencies, automatically download and include the library, manage project structure with the aim to make easier for developers to understand and work on projects, and build the project into JAR file.
Preliminary of SQL:
SQL, which stands for Structured Query Language, is a domain specific language that is used to manage and manipulate relational databases. Relational databases are organized into tables consisting of rows and columns, each of which can have relationship that allow for efficient retrieval and management of data. SQL is the language used for interaction between programs with relational databases. SQL allows us to extract specific information from the database (retrieve data), add new records to the database (insert data), change existing records (update data), delete tables and records from the database, define data (create modify and delete database structures), and manage user access and privileges (control data).
Preliminary of JavaFX:
JavaFX is a next generation open-source Java programming for client application platform that supports application development based on desktop, mobile and embedded systems.
A Step-by-step guide on how to import SQL libraries into JavaFX:
The background motivation why this tutorial needs to be provided is because there is a problem when the “import java.sql.*;” is implemented then the error warning will show the information about: package java.sql is not visible (see Figure 1).

Figure 1 The importing java.sql error.
The solution to handle this problem is composed of 2 steps that have to be done by the programmer.
The first step is to add the Maven repository artifact related to the MySQL connector to the pom.xml file, where the detailed information can be accessed in this link : https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java see Figure 2.
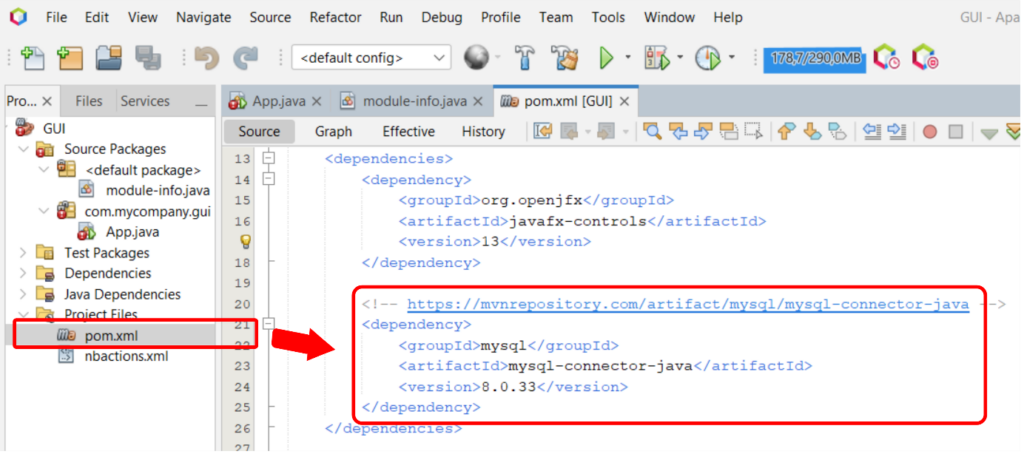
Figure 2 Adding the Maven repository to the pom.xml file.
The second step is to add “requires java.sql;” syntax to module-info.java (see Figure 3).
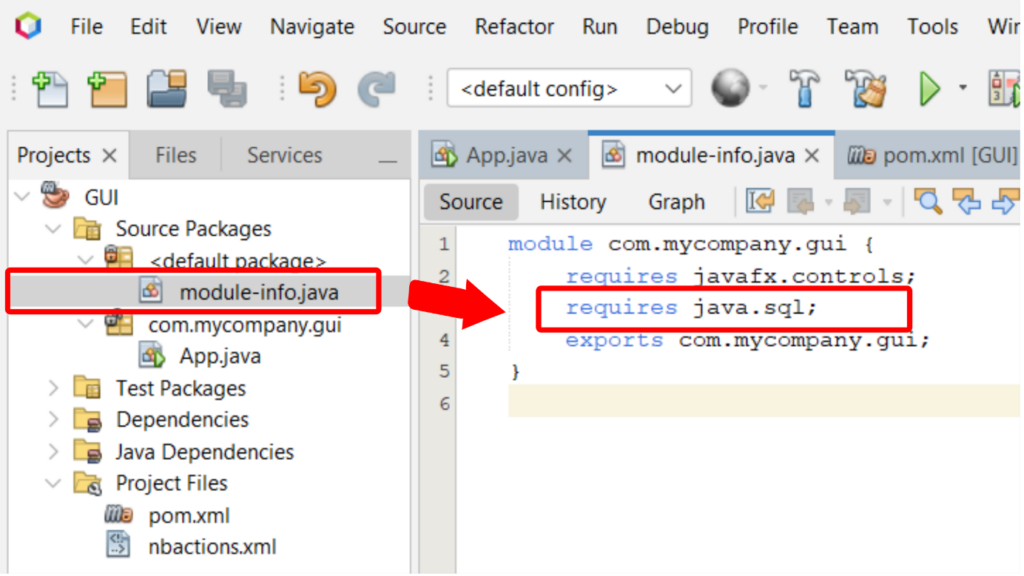
Figure 3 Tutorial on adding “requires java.sql;” syntax to module-info.java.
Now that the process of Figure 3 has been done, the import of java.sql can be done on App.java or any other Java class.




Comments :